Energy-efficient buildings are the trend, and green buildings will continue to develop rapidly.
Add time:
2016-09-19

Green buildings refer to buildings that maximize resource conservation (energy, land, water, and materials) throughout their entire lifecycle, protect the environment, reduce pollution, and provide people with healthy, usable, and efficient spaces that coexist harmoniously with nature. Green building encompasses planning, construction, and operation of solutions that are more efficient, healthier, and more sustainable than traditional solutions at equivalent levels of comfort and service throughout the building's life cycle.
China currently has over 50 billion square meters of existing buildings, and 1.6 to 2 billion square meters of new buildings are constructed annually. Over 95% of China's buildings are high-energy consumers. To achieve the same level of indoor comfort, the energy consumption per unit area of building is 2 to 3 times that of developed countries in similar climates. Energy efficiency renovations for existing buildings hold immense potential for energy conservation and emission reduction. During the 11th Five-Year Plan period, building energy efficiency accounted for 20% of all energy conservation tasks in China. If the 50% energy efficiency standard is effectively implemented, and the 65% standard is implemented in some areas, then by 2020, 354 million tons of standard coal could be saved annually, accounting for 30.7% of the national energy conservation target for that period. Green buildings, while achieving energy efficiency, can also provide users with a comfortable, healthy, and safe indoor environment, representing the global trend in building development, with a very promising future.
You may be interested in the following research: 2014-2020 Analysis Report on the Development Path and Investment Strategy Planning for China's New Urbanization Construction; 2014-2018 Analysis Report on the Development Prospect and Investment Strategy Planning for China's Urban Underground Pipeline Detection Industry; 2014-2018 Analysis Report on Market Prospects and Investment Planning for China's Waterworks Engineering Industry; 2014-2018 Analysis Report on Market Prospects and Investment Strategy Planning for China's Ceiling Industry; 2014-2018 Analysis Report on Market Prospects and Investment Strategy Planning for China's Parking Lot Construction Industry; 2014-2018 Analysis Report on Market Prospects and Investment Planning for China's Sea Dyke Engineering Construction Industry; More Research Reports >> According to the "2014-2018 Analysis Report on the Development Model and Investment Prediction for China's Green Building Industry" released by the Foresight Industry Research Institute, by the end of 2013, a total of 1260 green building evaluation mark projects were evaluated nationwide, including 480 one-star green building projects, 530 two-star green building projects, and 312 three-star green building projects. Following the explosive growth of the number of green building marks in China in 2011, the number of green building marks continued to show strong growth in 2012 and 2013.
Number of Green Building Projects in China (2008-2013) (Unit: Number of Projects)
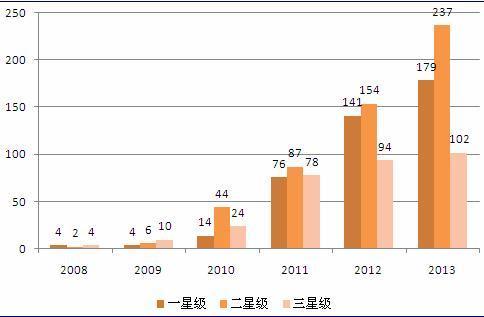
Data Source: Foresight Industry Research Institute
The scale of building projects in China that have obtained green building star energy efficiency labels is relatively small compared to other countries, but it is developing rapidly. The low level of development simultaneously implies that there is enormous market space for green buildings in China. Currently, investment enthusiasm for green buildings in China is concentrated in economically developed regions, particularly in Jiangsu, Shanghai, and Zhejiang in East China, which have a significant advantage nationwide in terms of both the number and scale of green buildings. This corresponds to Shanghai's leading position in GDP, per capita income, and purchasing power nationally. Guangdong in South China, and Beijing, Tianjin, and Hebei Province in Hubei also hold relatively high positions. The green building industry in these regions is developing rapidly, with relatively rich experience. Government policies for green buildings are more systematic and mature compared to other regions, market demand is becoming standardized, and the incremental cost of green buildings is relatively small, making them hot spots for green building investment.
In addition, the level of green building development in central and western China, and the northeast region, is relatively low, but this implies greater development potential. Once the government's policies on the development of the green building industry become more detailed, systematic, and effectively implemented, these regions will also become areas with significant potential for green building investment.